https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/https://www.rawpixel.com/image/9975640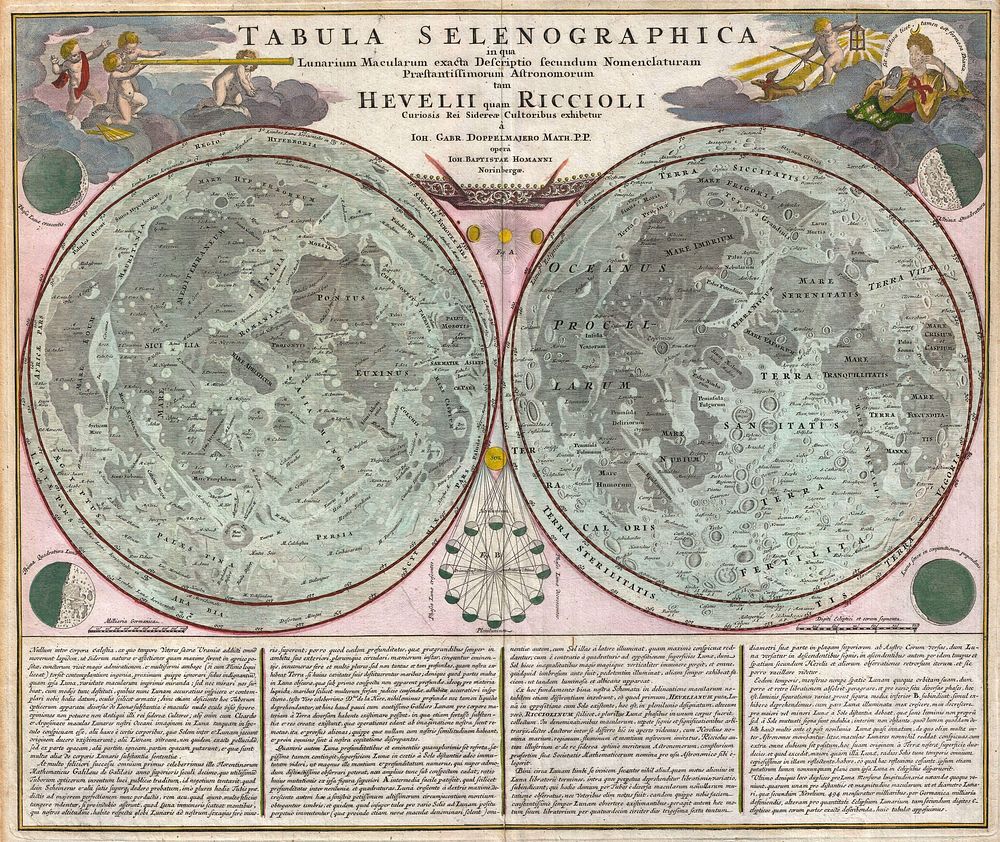

A stunning full color example of J. B. Homann and Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr’s important c. 1742 map of the Moon. Essentially a comparative chart, Doppelmayer constructed this map to illustrate the lunar mapping of Johannes Hevelius (left) and Giovanni Battista Riccioli (right). The left hand lunar map, composed by Hevelius, is a considered a foundational map in the science of Selenography – or lunar cartography. This map first appeared in Hevelius’ 1647 work Selenographia which laid the groundwork for most subsequent lunar cartographic studies. Here the moon is presented as it can never be seen from Earth, at a greater than 360 degrees and with all visible features given equal weight. In this map Hevelius also establishes the convention of mapping the lunar surface as if illuminated from a single source – in this case morning light. The naming conventions he set forth, which associate lunar features with terrestrial locations such as “Asia Minor”, “Persia”, “Sicilia”, and etcetera were popular until the middle of the 18th century when Riccioli’s nomenclature took precedence. The Riccioli map, on the right, is more properly known as the Riccioli-Grimaldi map, for the fellow Jesuit Francesco Grimaldi with whom Riccioli composed the chart. This map first appeared in Riccioli and Grimaldi’s 1651 Almagestum Novum . This was a significant lunar chart and offered an entirely new nomenclature which, for the most part, is still in use today. Curiously, though Riccioli, as a devout Jesuit, composed several treatises denouncing Copernican theory, he chose to name one of the Moon’s most notable features after the astronomer – perhaps suggesting that he was a secret Copernicus sympathizer? Other well-known lunar features named by Riccioli include the Sea of Tranquility where Apollo 11 landed and where Neil Armstrong became the first human to set foot on the moon’s surface. The upper left and right hand quadrants feature decorative allegorical cartouche work that include images of angelic children looking through a telescope and a representation of the ancient Greek Moon goddess Selene. Additional mini-maps show the moon in various phases of its monthly cycle. Below the map proper extensive Latin text discusses Selenography. This map first appeared in J. B. Homann’s 1707 Neuer Atlas and was later reissued as plate no. 11 in Doppelmayr’s important 1742 Atlas Coelestis , which was also published by the Nuremburg firm of Johann Baptist Homann. There is no discernable difference between the two issues and it is all but impossible to know in which of the two publications this map was drawn from.
Original public domain image from Wikimedia Commons
Public DomainFree CC0 image for Personal and Business use