https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/https://www.rawpixel.com/image/7665314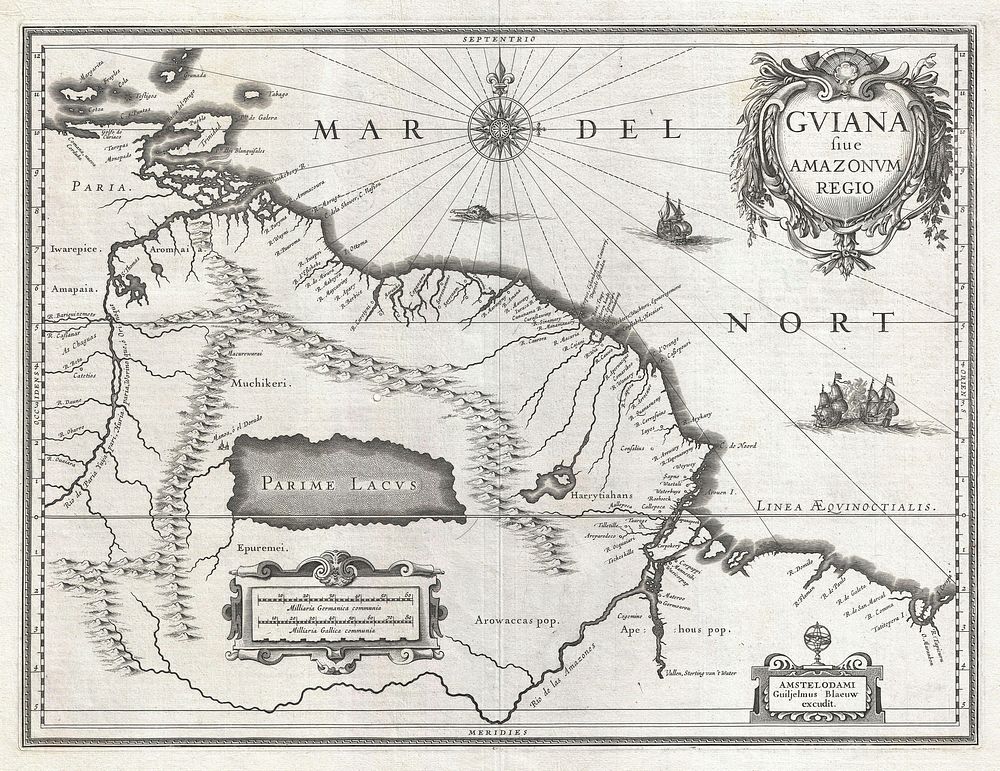

This is G. Blaeu's remarkable c. 1635 map of the northeastern parts of South America , Lake Parima (Parime Lacus), and the route to El Dorado. Blaeu initially issued this map in 1630 and variants were published well in to the 1660s. This example dates to the 1635 German edition of Blaeu's atlas. The map covers from Isla Margarita and the Orinoco Delta eastward as far as Tampico and southwards as far as the Amazon River. This region of South America generated considerable European interest in the early 17th century following the publication of Sir Walter Raleigh's fascinating Discovery of the Large, Rich, and Beautiful EMPIRE Of GUIANA . Raleigh's expedition traveled down the Orinoco River in search of the Kingdom of El Dorado. Today we know that El Dorado did not exist, but was rather an amalgam of very real tribal traditions and the European lust for gold. Nonetheless, in the 16th century, tales of El Dorado were common conversation along the port cities of the Spanish Main. Having explored a considerable distance down the Orinoco, Raleigh's expedition found itself mired in a remote tribal village at the onset of the rainy season. While waiting for an opportunity to return north, a trading delegation arrived. At this time the dominate trading empire in the Amazon were the Manoa, who, though based near modern day Manaus, pursued trade routes to from the foothills of the Andes to the Amazon and Orinoco Deltas. While the rainy season prevented Raleigh from moving forward, for the Manoa it had the opposite effect. The heavy rains inundated the vast Parima flood plain creating a great inland sea, consequently opening an important trade connection between the Amazon and Orinoco Rivers. When the Manoa arrived, Raleigh and his men noticed that they had various golden trinkets for sale. This was apparently enough for Raleigh to deduce that they must indeed be from the hidden kingdom of El Dorado. When Raleigh asked where the traders came from, the locals, with no common language with which to engage Raleigh, could only explain that they traveled across a great water and were from Manoa. Raleigh's presumptuous narrative inspired many early cartographers to map this massive lake, with the city of El Dorado or Manoa on its shores, in the unexplored lands between the Orinoco and Amazon River basins. In addition to Blaeu's fascinating depiction of Lake Parima, among the most prominent such in any mapping of this region, there are also a number of attractive decorative elements. Three sailing ships ply the waters and just under the compass rose a scary looking sea monster swims toward shore. A decorative baroque title cartouche appears in the upper right quadrant and, at the bottom of the map, to small cartouches frame a distance scales and Blaeu's signature. Uncolored as issued.
Original public domain image from Wikimedia Commons
Public DomainFree CC0 image for Personal and Business use